The Principle of Nominality
Here we examine how JM Hurst arrived at the framework we often use to perform phasing analysis on financial markets
What is Nominality?
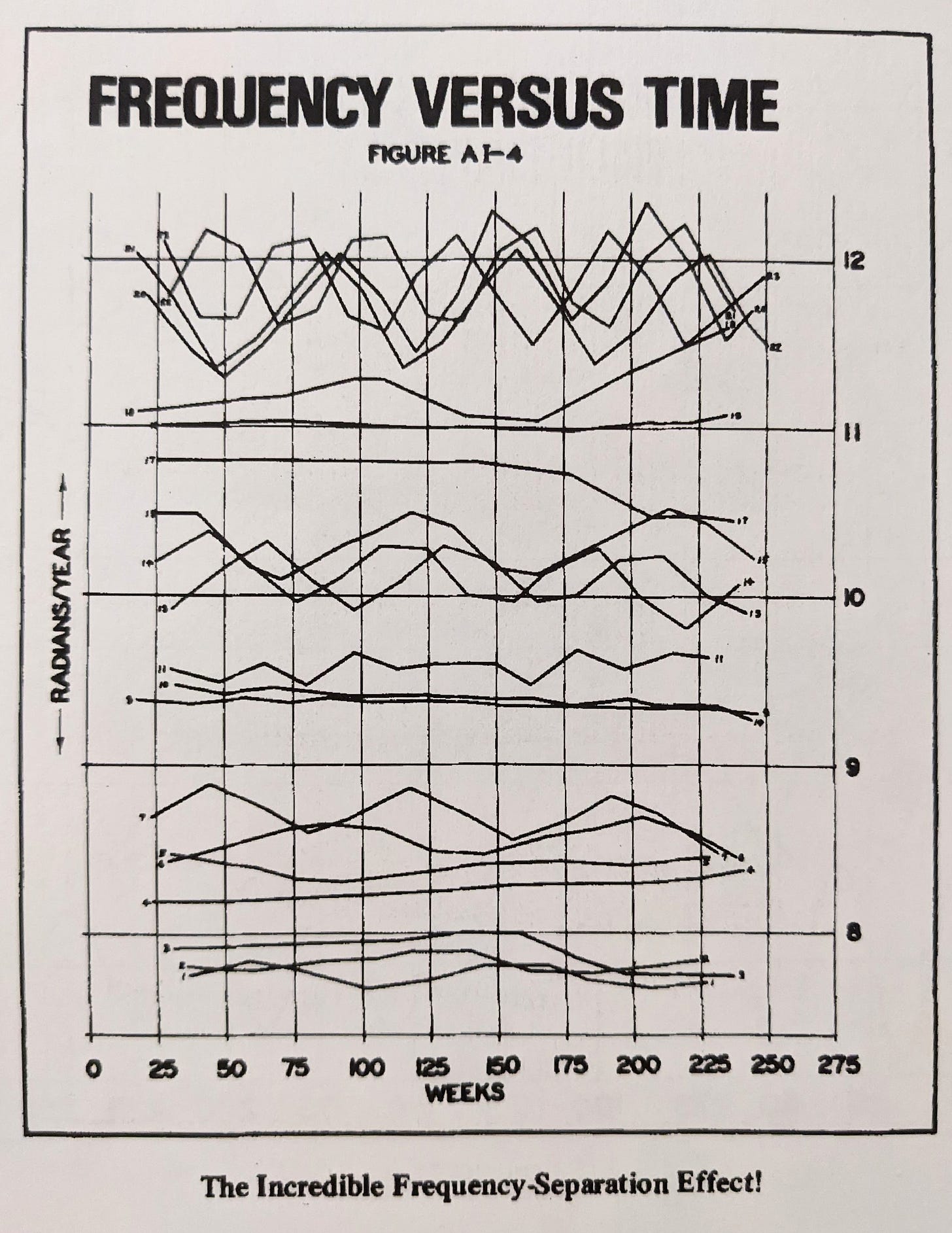
The term ‘nominal’, in relation to Hurst Cycles, refers to the distinct naming convention of groups in Hurst’s nominal model. These are a collection of groups that coalesce around similar frequencies, named for ease of use and convention. In reality, periodic functions in financial markets are plagued by all kinds of variation, excursions from the nominal model groups are described by the principle of variation. These variations are comprised of both frequency and amplitude modulation. Hurst referred to this variation as ‘magnitude-duration-fluctuation’. Catchy!
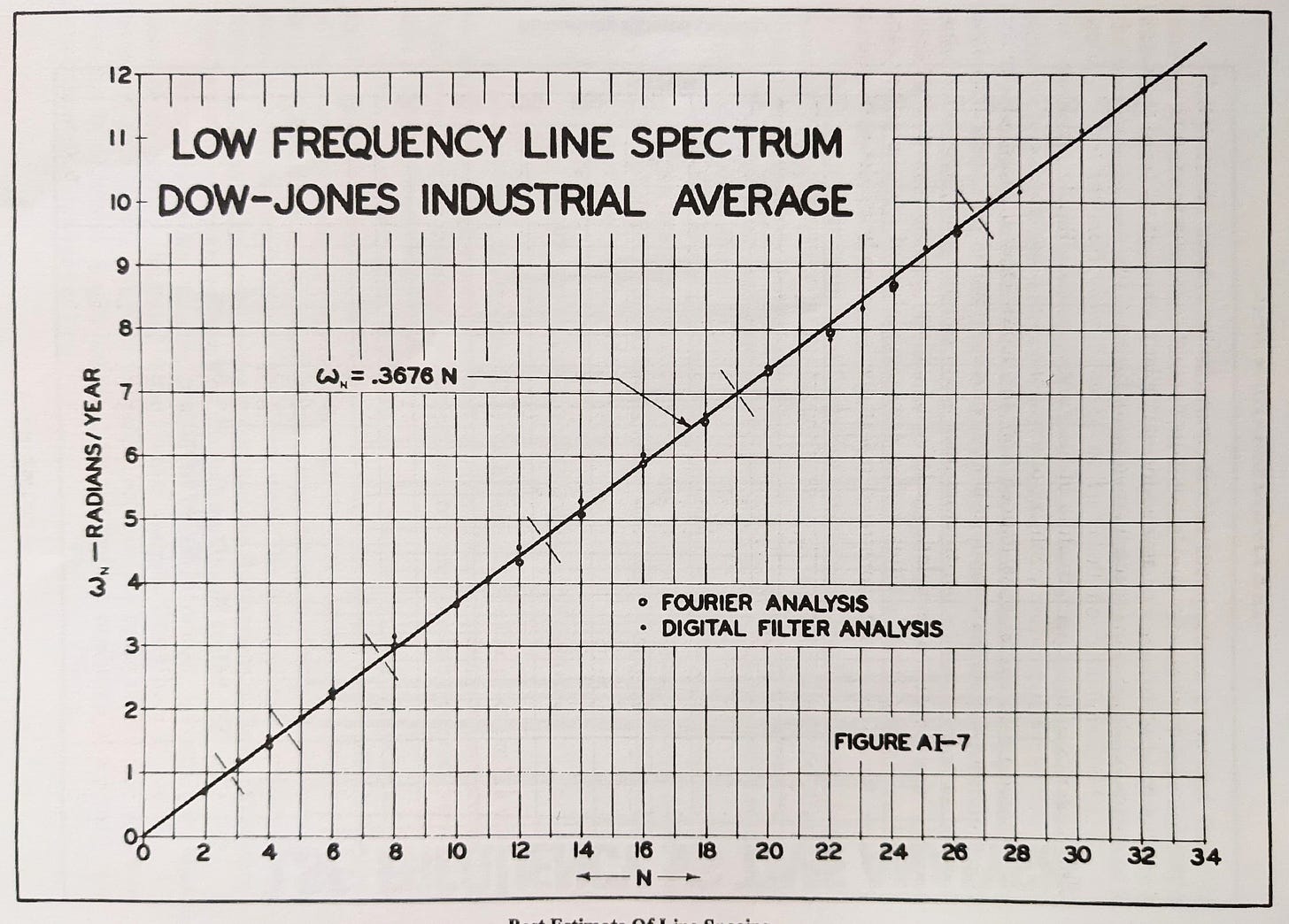
Importantly, Hurst found in his research that the grouping of component frequencies exhibited in stockmarkets (and commodities later in the Cycles Course) show distinct spectral spacing. Another way to describe the spacing of frequencies is that of a non normal distribution. The latter might indicate that markets are infact entirely explained by ‘pink noise’ - the type of noise that displays a distinct ‘1/f’ magnitude spectrum in the frequency domain. The spectral spacing gave rise to the grouping described above and the resulting nominal model. The groups within the nominal model can also be thought of as ‘carrier’ frequencies, each one consisting of finer frequencies closely related to the carrier and suitably amplitude modulated.